1. Background
Mobile phones as a portable device are available at any time or place. They are an ideal medium and people’s interest in the use of mobile apps in various fields has increased. One of the most popular areas is health, and apps in this field are modifying the lifestyle of people (1, 2). mHealth is defined by WHO as “an area of electronic health (eHealth) and it is the provision of health services and information via mobile technologies such as mobile phones and Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs)” (3). Every year, many mHealth apps are developed in the health field for different clinical conditions (4-8). Prediction indicates significant growth in mHealth apps development and introduction in health fields, as a top priority for application developers (9). There are different motivations for publishing mHealth apps. Helping people to improve health conditions, generating revenue, and data gathering are the most important goals of mHealth app developers. The mHealth app market is very young and attracts more newcomers every day. Although this market has a high potential, a limited percentage of developers achieve their business goals. Research2Guidance report shows competition in mHealth on the Production side (number of published apps) is growing faster than the requirement side (app downloads) (10). There is high failure risk for mHealth app developers with little or no experience in the field of health and lower income levels.
Some applications are rarely downloaded by users, while some other apps have been downloaded and installed more than several ten thousand times (11). To date, a few studies have characterized effective factors that influence the number of app downloads by users. Most of these surveys have only studied factors affecting the number of application downloads from the economical aspect (12-16). A few studies have considered some non-commercial influential factors. Mobile application developers submit several screenshots of the app with short description about features and functionality of the program at the time of publishing the application on the app store. These uploaded images and descriptions written about the app affect the user's decision when choosing apps for download (12, 17). Studies have shown that the size of mobile apps is inversely related to the number of downloads (13, 15). Large file size takes a long time to download and occupies additional space, thus increasing size of mobile apps reduces download count. Another survey pointed the time elapsed since published date of apps impacts the number of downloads, because app’s age is an indicator for chance of user awareness. Releasing a new version of the app, in which the features of the program is updated, has a positive impact on the number of downloads (13). A recent study aimed at detecting predictors of urology app downloads (18). It only focused on urology-related scopes and reviewed 129 apps. The results of this study showed that applications with lower price, higher rating value, and greater number of reviews written by users were more likely to be downloaded. According to the results obtained from the analysis of most popular apps, developers can improve their design to develop and publish more user-friendly apps, which are closer to preferences of end users.
Cafebazaar is the largest Persian Android app store with more than 3500 apps in medical and health categories. Most Iranians download apps from this app store (19). The main aim of this study was to detect economic and non-economic predicators of mHealth apps download from the most popular Persian app store.
2. Methods
The researchers gathered information of all apps in two categories, health and medicine, in Cafebazaar as the most popular Persian Android app store up to November 20th, 2016. They wrote a program with PHP (which is a server-side scripting language) and MySQL database (version 5.6) to check the Cafebazaar app store website and gathered available information of published medical apps, automatically. The researchers checked all apps and excluded apps not related to health and medicine. In the next step, they excluded apps with missing value. All missing values appeared in rating value and rating count fields. Based on all available information, nine pre-determined variables were selected. All selected variables and their descriptions are listed in Table 1.
| Variables | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Number of app downloads | Number of apps being downloaded and installed |
| 1 | < 100 |
| 2 | 100 - 200 |
| 3 | 200 - 500 |
| 4 | 500 - 1000 |
| 5 | 1,000 - 2,000 |
| 6 | 2,000 - 5,000 |
| 7 | 5,000 - 1,0000 |
| 8 | 10,000 - 20,000 |
| 9 | 20,000 - 50,000 |
| 10 | 500,00 - 100,000 |
| 11 | 100,000 - 200,000 |
| 12 | 200,000 - 500,000 |
| 13 | > 500,000 |
| Rating count | Number of rates in the Bazar app store |
| Rating value | User evaluation on a scale from 1 to 5 stars |
| App size | Application file size |
| App price | Price of the app in Rials |
| In-app purchase | |
| 0 | No in-app purchase |
| 1 | In-app purchase available |
| Length of app name | Number of characters |
| Using Internet | |
| 0 | App doesn’t connect to Internet |
| 1 | App connect to Internet |
| Using camera | |
| 0 | Camera is not available |
| 1 | Camera is available |
| Using location or GPS | |
| 0 | Location and GPS is not available |
| 1 | Location and GPS is available |
| Number of released apps by a company | Number of other apps developed by this company |
Predetermined Variables to Predict the Number of mHealth Apps Active Installation
Because the exact number of downloads were not available in Cafebazaar app store, the researchers categorized them according to the classification system grade of installations used by this app store. Descriptive analysis and multivariate ordinal logistic regression were used to evaluate the effect of variables on the number of app downloads. Analysis was performed using Microsoft Excel 2010 and SPSS version 22 and P value values of < 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
3. Results
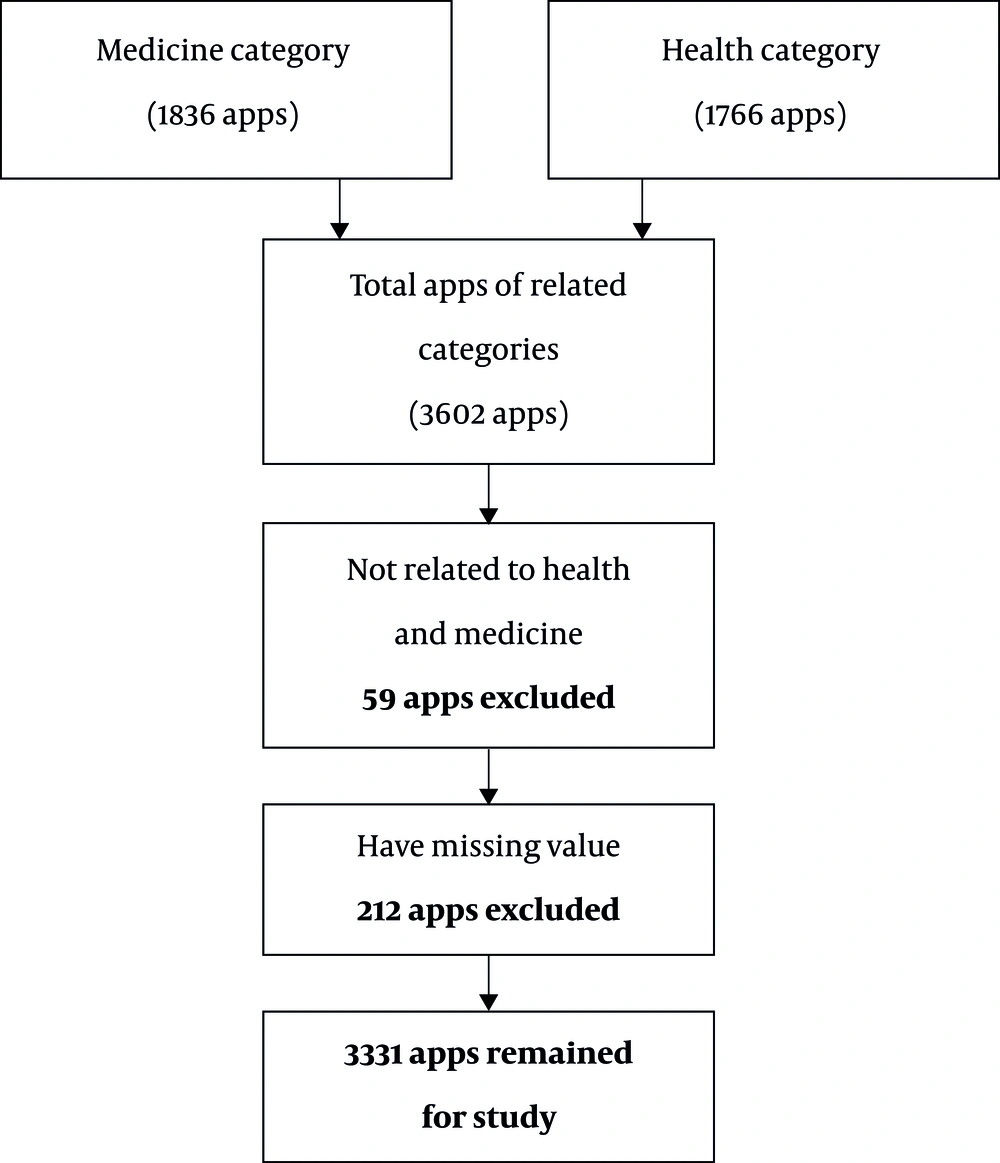
Information of 3602 apps (1836 apps from medicine category and 1766 apps from the health category) were gathered and 271 apps were excluded in two steps. Figure 1 shows the number of apps excluded at each step.
Of the 3331 remaining apps, 24.4% were paid apps with prices ranging from 10,000 Rials to 300,000 Rials. Minimum and maximum number of apps developed by a person or company were one and 36, respectively (average of eight apps). The average of rating value for all of the apps was 4.26 and number of ratings ranged from one to 39,359. Descriptive statistics for continuous variables with more details are listed in Table 2.
| Range | Median | IQR | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rating count | 1 - 39359 | 25 | 92 |
| Rating value | 1 - 5 | 4.40 | 0.7 |
| App size (KB) | 71 - 94275 | 2626 | 2970.5 |
| App price (Rials) | |||
| All apps | 0 - 300,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Paid apps | 10,000 - 300,000 | 20,000 | 10000 |
| Number of released apps by a company | 1 - 36 | 4 | 11 |
| Length of app name (character) | 2 - 44 | 15 | 10 |
Descriptive Statistics for Continuous Variables
Frequencies for the categorical and binary variables are listed in Table 3. Overall, 32% of apps had in-app purchase available. Furthermore, 2400 apps (72%) could connect to the Internet. Location-based services like GPS was available in 121 apps and only 2% of apps used the camera.
| Variables | Frequency | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of app downloads | ||
| 1: < 100 | 430 | 12.89 |
| 2: 100 – 200 | 330 | 9.90 |
| 3: 200 – 500 | 592 | 17.75 |
| 4: 500 – 1000 | 441 | 13.22 |
| 5: 1,000 - 2,000 | 554 | 16.61 |
| 6: 2,000 - 5,000 | 618 | 18.53 |
| 7: 5,000 - 10,000 | 191 | 5.73 |
| 8: 10,000 - 20,000 | 90 | 2.70 |
| 9: 20,000 - 50,000 | 64 | 1.92 |
| 10: 50,000 - 100,000 | 16 | 0.84 |
| 11: 100,000 - 200,000 | 5 | 0. 15 |
| 12: 200,000 - 500,000 | 3 | 0.09 |
| 13: > 500,000 | 1 | 0.03 |
| In-app purchase | ||
| 0 : No in-app purchase | 2258 | 68 |
| 1 : In-app purchase available | 1077 | 32 |
| Using Internet | ||
| 0 : App doesn’t connect to Internet | 935 | 28 |
| 1 : App connect to Internet | 2400 | 72 |
| Using camera | ||
| 0 : Camera is not available | 3275 | 98 |
| 1 : Camera is available | 60 | 2 |
| Using location or GPS | ||
| 0 : Location and GPS is not available | 3214 | 96 |
| 1 : Location and GPS is available | 121 | 4 |
Frequencies of the Categorical and Binary Variables
The most number of app downloads were in four grades (grade 3 to grade 6), which is greater than 200 and less than 5000 (66%). Only one app was downloaded more than 500,000 times. Ordinal logistic regression was used to identify predicators of mHealth app downloads. The results are shown in Table 4. Apps with a higher number of ratings were more likely to be installed (P value < 0.001). Availability of Internet (P value < 0.001) and using the camera (P value = 0.03) were also significantly associated with the app download. The number of apps developed by a company or person and app price were inversely related to the number of app downloads (P value < 0.001).
| Coefficients | Standard Error | P Value | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rating count | 0.000551 | 0.000028 | < 0.001 | 0.00049 to 0.00061 |
| Rating value | 0.011975 | 0.050274 | 0.812 | -0.0866 to 0.11 |
| App size (KB) | -0.000010 | 0.000006 | 0.059 | -0.00002 to 0.0000004 |
| App price (Rials) | -0.000037 | 0.000002 | < 0.001 | -0.000042 to -0.000032 |
| In-app purchase | -0.103651 | 0.078617 | 0.187 | -0.2577 to 0.0504 |
| Length of app name | 0.007451 | 0.004332 | 0.085 | -0.001 to 0.015 |
| Using Internet | 0.564251 | 0.078488 | < 0.001 | 0.4103 to 0.7181 |
| Using camera | 0.556132 | 0.264556 | 0.036 | 0.0374 to 1.0748 |
| Using location or GPS | 0.082138 | 0.191508 | 0.668 | -0.293 to 0.457 |
| Number of released apps by a company | -0.018805 | 0.004281 | < 0.001 | -0.0272 to -0.0104 |
Predicators for mHealth App Downloads as a Result of Ordinal Logistic Regression Analyses
4. Discussion
In the current study, different available factors were considered to detect predicators of mHealth apps download from one of the most popular Persian app stores. There is detailed information about published applications on most app store web sites. These information are available on app store websites to the public and you do not need to use a questionnaire to gather these factors. Therefore, analyzing these available factors as valuable resources can be used to forecast the app market.
The mHealth app market is a growing market and there is an increasing competition between mHealth app developers in this market. Some apps are downloaded over 10,000 times, while some others have been downloaded less than 100 times. This heavy competition on the supply side of mHealth to gain market share has led developers to pay greater attention to customers' needs and companies should have a more accurate forecast of the target market. The results of the current study characterized some factors influencing the number of mHealth app downloads. App stores are the most popular platform for the distribution of mHealth apps (20, 21). There is considerable information about published apps in app stores, which distinguishes them from traditional software deployment mechanisms. User feedback about the released apps is one of the most valuable resources for analyzing customer behavior. Many previous studies have pointed to customer feedback as a considerable information resource (22-24). The current results showed that apps with higher number of submitted comments were more likely to be installed. Previous studies mentioned that number of registered reviews on the Internet affects product sales and is considered as a predicator for the number of mobile app downloads (13, 14). Although users declare their feedback about an application in a variety of ways, such as submitting comments and rating, impact of each one is different. In the comments, application users can express their opinions with more details clearly. Therefore, it has a greater impact on users, who intend to download and install the app. Rating value of apps has a positive effect yet is not significant. This may be due to poor user attention towards app ratings. The results of the current study showed that price of apps is another predicator. Application price was inversely related to the number of app downloads, where inexpensive apps were more likely to be installed.
Users preferred apps, which could connect to the Internet and updated their content periodically (11, 25, 26). Also, Internet and camera usage were indicators of social mHealth apps. Users can take pictures and share their health information and photos with family and friends on social networks. The results of the current study showed that Internet and camera usage are influential factors on application downloads. Apps that provide these features are popular and more likely to be installed. Results of the current analysis showed that the number of apps developed by a company or person was inversely related to the number of app downloads. There is a feature in most of app stores, which recommends other apps to be published by a developer. In most studied cases, previous released apps by a developer have a low quality and poor feedback. This study indicates that several variables, such as size of application, length of app name, and application purchase type have no significant impact on the number of downloads. Although some studies on generic mobile apps pointed these mentioned variables as predicators (12, 13, 15), the current study confirmed the results of previous studies on mHealth, which was done on urology apps (18). Developers are struggling to achieve their goals yet the majority are not making money with mHealth apps (11). Based on predicted number of downloads, developer companies can estimate their future revenue. Also, the obtained predicators help developers define their marketing strategies based on target groups, such as pricing apps and scope of advertising.
4.1. Limitation
The current study had some limitations. In this study, only published mHealth apps in Cafebazaar, as the main Persian market for Android apps, were reviewed. The researchers did not review the content of user comments. Some users praise the app and announce their satisfaction, and a number of other users may have negative comments and have expressed the app's bugs. Other variables, such as age of application or version number of app have been reported as predicators for number of app downloads in some previous studies. These variable were not available in Cafebazaar as the proposed app store. Therefore their effects could not be considered in the current study.