1. Context
Several studies declared a significant correlation between academic achievement as a behavioral index and happiness among Iranian students (1). For Canadian students in 2005, a relationship was also reported between academic achievement and happiness (2). Higher academic achievement was also observed in teenagers with more happiness feeling (3, 4). Currently, there is no integrated study to gather all data from published articles through a meta-analysis approach. Meta-analysis is a quantitative study that uses published research to make a firm conclusion. A meta-analysis uses specific statistical procedures to estimate the effect of risk factors on the system better than individual studies do. Therefore, a meta-analysis integrates the outcomes of independent research to obtain reliable trends across the studies. Nevertheless, there was no comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis on the factors affecting students’ academic achievement and their relationship with students’ happiness in Iran. Regarding multiple studies concerning the factors influencing academic achievement in university students, a meta-analysis seemed necessary to pool and validate the results of available studies and provide a more precise guide for researchers and policymakers in the field (5, 6).
2. Objectives
The present study aimed to explore the relationship between happiness and academic achievement in students using a systematic review and meta-analysis approach. We also aimed to categorize the influencing factors based on their type and study field.
3. Evidence Acquisition
This study was a systematic review and meta-analysis. The data were gathered from studies performed across the world. The literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Google Scholar, and Web of Knowledge databases using keywords including students, happiness, and effective factors, as well as their Persian equivalents in 2013 - 2017.
4. Study Selection and Qualification
The STROBE checklist (3) was utilized for screening the papers. Each item of the checklist was scored from 0 to 2 independently by two of the authors. Accordingly, the studies were categorized into either of the poor, moderate, and good groups corresponding to 1 - 15, 16 - 30, and 31 - 44 scores, respectively. Studies reaching at least the score 16 (i.e. well-designed studies) were included in the meta-analysis.
4.1. Study Selection and Data Extraction
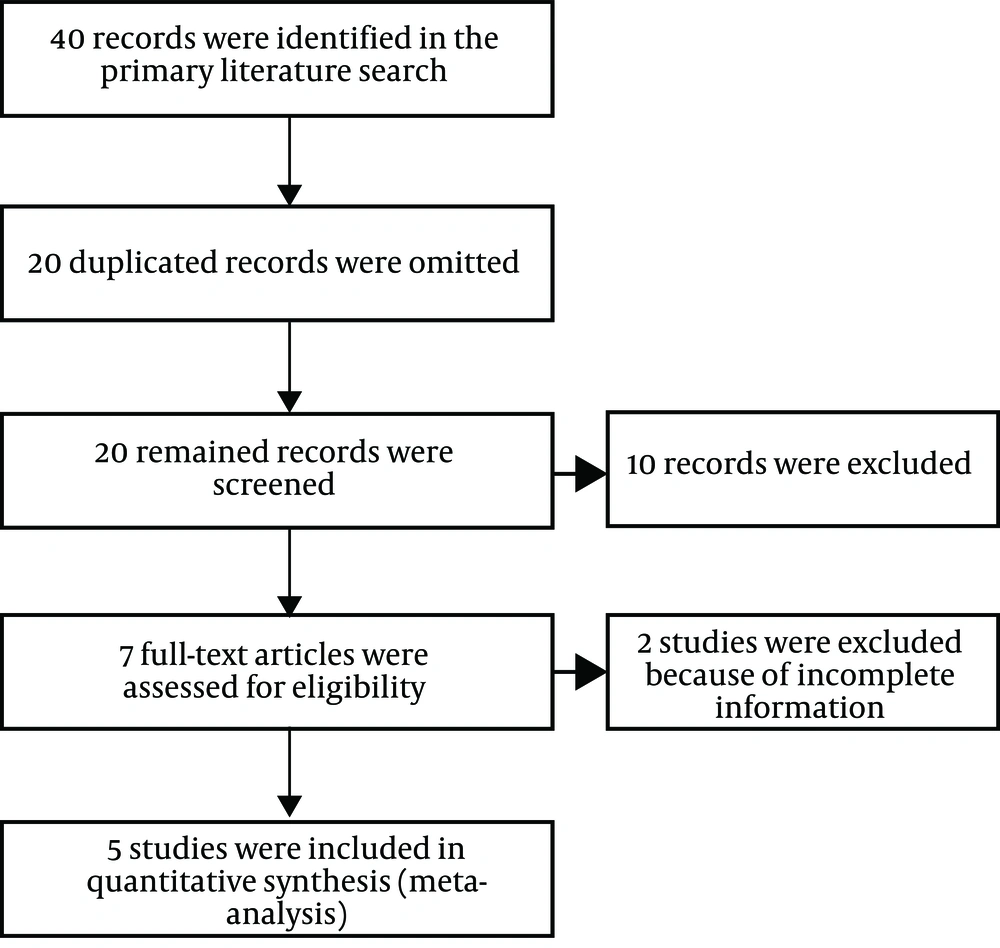
Initially, the researcher searched for Iranian studies of the effective factors on students’ happiness and academic achievement. After the literature search, a checklist of related abstracts was prepared. We selected all the articles with “academic achievement” and “student happiness” and “regression” and “correlation” in their titles. Articles related to academic failure and associated factors were omitted at this stage. In the next step, these studies were re-evaluated for final inclusion in the meta-analysis, as shown in the study flowchart in Figure 1.
4.2. Statistical Analysis
Considering the high heterogeneity between studies (demonstrated by statistically significant heterogeneity index (I2)), a random-effects model was utilized for meta-analysis. The data were analyzed using STATA (version 11.1).
5. Results
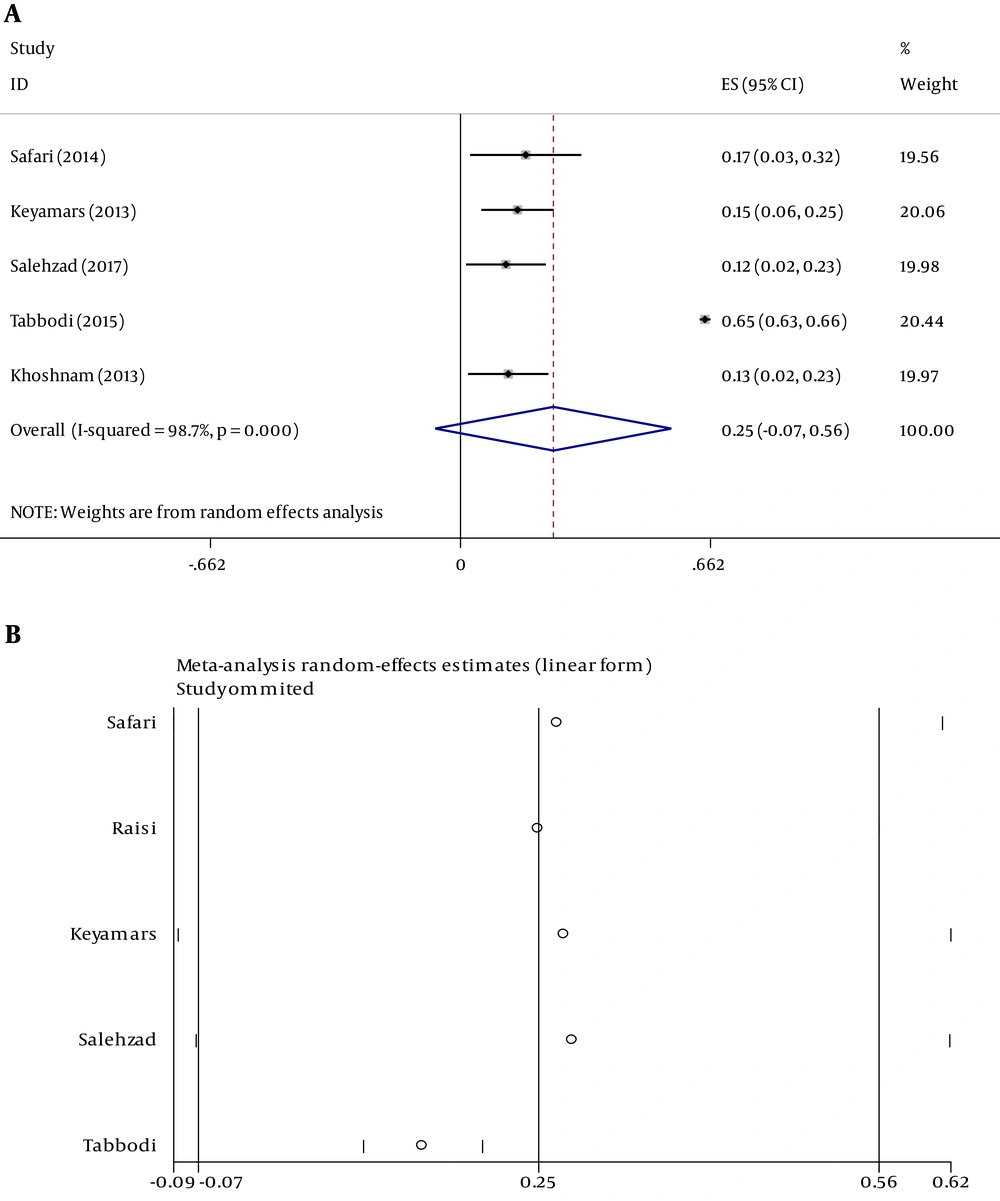
Figure 2 shows the association between academic achievement and happiness scores in both school and university students. Considering the correlation coefficient within -1 ≤ r ≤ 1 and the non-normal distribution of the coefficient, the value was normalized by applying following equation.
Then, the standard deviation was calculated using
Forest plot of the relationship between academic achievement and happiness scores in school and university students with a 95% confidence interval. A) The mean correlation coefficient between academic achievement and happiness scores obtained as z = 0.25 (95% CI: 0 - 7.56, I2 = 98.7%) r = 0.24 (95% CI: 0 - 50) in university students. B) Sensitivity analysis of the correlation between happiness an academic achievement in students.
Sensitivity analysis showed that the study by Tabbodi was influential so that it remarkably changed the obtained results of in the current study (Figure 2B). Table 1 shows the characteristics of the articles examining the relationship between academic achievement and happiness in students.
| Authors (Ref.) | Year | City in Iran | Total Sample Size | Female (N) | Male (N) | Academic Achievement Score | Happiness Score | Study Group | Job |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Safari et al. (7) | 2014 | Tehran | 180 | 36 | 144 | 61.6 | 12.65 | University students | Medical, nursing and midwifery |
| Kiamarsi and Momeni (8) | 2013 | Ardabil | 420 | 420 | 0 | 47.4 | 15.99 | High school students | High school |
| Salehzadeh et al. (9) | 2017 | Yazd | 350 | 350 | 0 | - | - | University students | High school girls |
| Tabbodi et al. (10) | 2015 | Shiraz | 18465 | 10235 | 8230 | 57.5 | 15.89 | University students | Students of Azad University of Medical Sciences |
| Khoshnam et al. (11) | 2013 | Tehran | 341 | 211 | 130 | 50.04 | 16.75 | High school students | High schooler |
aSince the studies did not use the same tools, the extracted data were homogenized by multiplying them in certain coefficients so that the data of all studies were comparable; thus, a better comparison could be made.
The obtained results in the current study were in line with those by Robbins et al. (12) and Wei et al. (13). Lower happiness scores were reported from Kuwait and England than the international scores (14, 15). Students with higher levels of happiness were found to place in the category of higher academic achievement and health by Walton and Cohen (16). There are also other studies reporting higher mean scores for happiness than the mean score found in the current study (17, 18).
6. Conclusions
In spite of the interaction of happiness with academic achievement, yet no correlation has been reported between these parameters. Academic achievement can lead to student’s satisfaction and happiness. Mentally healthy students with suitable levels of happiness obtain better results in terms of education and academic performance (7, 19). Happiness also improves students’ academic achievement; thus, this effective factor should be considered for improving the students’ performance.