1. Background
Sleeping is a physiological need for the body, which plays critical role in efficient functioning of the body organs and is a vital factor contributing to mental and physical health (1, 2). Sleep problems are the most important public health issues. Poor sleep quality has different physical and psychological consequences such as fatigue, behavioral disorders, cardiovascular disease, decreasing memory and concentration, as well as aggression and violence (3-5).
Sleep disorder has been increasing among university students such that, according to a meta-analysis study, the overall prevalence of poor sleep quality in Iranian students is 56% at present (6). Poor sleep quality can affect students' academic achievement (7) in addition to their physical and mental performance. Therefore, it is important to examine the students’ sleep quality and identify its effective factors.
Various factors influence sleep quality. According to extensive studies from the literature, several factors including age, sex, marital status, type of residence, anxiety, depression, smoking, alcohol use, drug use, BMI, smartphone dependence as well as health-related behaviors such as nutrition and stress management affect the quality of sleep (8-13).
There is inadequate published studies about students’ sleep quality and its contributory factors in the literature on different medical disciplines (e.g., medicine sciences, health sciences, etc.), especially longitudinal studies. Majority of the previous studies have only explored the students of one particular discipline (e.g., Nursing, Medicine, or Pharmaceutics) (14-17). The current study aimed to investigate the students' sleep quality and its underlying factors by using the information from the first baseline data included in the “Health and Lifestyle of University Students” (HeLiS).
2. Objectives
Our study was the first longitudinal study conducted in Tabriz, Iran, to explore Iranian medical university students.
3. Methods
In order to examine the association between sleep quality and its underlying factors, the data related to sleep quality and demographic characteristics were extracted from baseline information found in the Health and Lifestyle of University Students (HeLiS). The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), a self-administered questionnaire containing general information about sleep quality, Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), a questionnaire consisting of information about anxiety, Healthy Lifestyle Scale for University Students (HLSUS), and a questionnaire consisting of information about lifestyle were completed by students during the first eight weeks of their first semester.
3.1. Study Population
The HeLiS was the first longitudinal study on Iranian university students. This study aimed to investigate the influence of anxiety, lifestyle and demographic information on sleep quality among students of different medical fields. All first-year students of different medical fields studying in eight university schools who had enrolled in September 2014 were requested to participate in this study. The inclusion criteria were: enrolled students aged under 25 years, undergraduate students of dentistry, pharmaceutics and medicine, and students willing to participate in the follow-up study. At first, the participants were requested to answer a self-report questionnaire with minimal instruction which took about 40 minutes to complete.
The study questionnaire consisted of demographic status, sleep quality, anxiety, and lifestyle measures. Sleep quality, anxiety, and lifestyle were assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI), Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI), and Healthy Lifestyle Scale for University Students (HLSUS) questionnaires, respectively.
The PSQI is a 19-items instrument to distinguish the good sleep quality from the poor sleep quality by assessing seven sleep characteristics including subjective sleep quality, sleep latency, sleep duration, habitual sleep efficiency, sleep disturbances, use of sleep medications, and daytime dysfunction. Higher values for PSQI total score indicate lower sleep quality, such that a score of 5 or higher indicates poor sleep quality.
The BAI contains 21 items whose answers are scored on a scale value of 0 (not at all) to 3 (severely). Higher values for BAI total scores indicate more severe anxiety symptoms.
The HLSUS contains 38 questions whose answers are scored on a scale value of 1 to 5. This instrument specifies students' lifestyle by assessing eight dimensions, including exercise behavior, regular behavior, nutrition behavior, health risk behavior, health responsibility, social support, stress management, and life appreciation. Higher total scores for HLSUS indicate healthier lifestyle (18).
After preparing the data collection instrument, oral consent was received from the students; then they were asked to complete the questionnaires.
3.2. Statistical Analysis
Data were described as mean ± SD of numeric and frequency (per cent) for categorical variables. Panel linear regression (PLR) and frontier model (FM) were used to investigate the relationship between sleep quality, the primary outcome of the study, as well as students' anxiety, lifestyle, and demographic information. PLR and FM were compared using Akaike information criteria (AIC) and Bayesian information criteria (BIC), where smaller values of AIC and BIC was indicative of more powerful model. Finally, the results of more powerful model were reported.
Analyses were performed using STATA MP 15.0 (StataCorp. 2017. Stata Statistical Software: Release 15. College Station, TX: StataCorp LLC).
4. Results
4.1. Participants' Profile
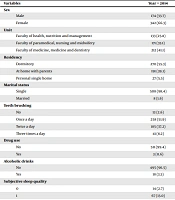
A total of 516 students in 2014, 619 students in 2015, and 373 students in 2016 were included in the study. Mean score of PSQI among the students was 5.25 (SD = 2.00), so that it was equal to 6.34 (SD = 1.17) in 2014, 4.15 (SD = 2.28) in 2015, and 5.56 (SD = 2.91) in 2016. A total of 323 students (62.6%) in 2014, 212 ones (34.2%) in 2015, and 171 ones (47.8%) in 2016 had poor sleep quality. The details of the participants' characteristics are shown in Table 1.
| Variables | Year = 2014 | Year = 2015 | Year = 2016 | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 174 (33.7) | 215 (34.7) | 110 (29.5) | 499 (33.1) |
| Female | 342 (66.3) | 404 (65.3) | 263 (70.5) | 1009 (66.9) |
| Unit | ||||
| Faculty of health, nutrition and management | 133 (25.8) | 133 (21.5) | 99 (26.5) | 365 (24.2) |
| Faculty of paramedical, nursing and midwifery | 171 (33.1) | 223 (36.0) | 145 (38.9) | 539 (35.7) |
| Faculty of medicine, medicine and dentistry | 212 (41.1) | 263 (42.5) | 129 (34.6) | 604 (40.1) |
| Residency | ||||
| Dormitory | 270 (55.3) | 264 (55.5) | 166 (56.1) | 700 (55.5) |
| At home with parents | 191 (39.1) | 186 (39.1) | 114 (38.5) | 491 (39.0) |
| Personal single home | 27 (5.5) | 26 (5.5) | 16 (5.4) | 69 (5.5) |
| Marital status | ||||
| Single | 508 (98.4) | 592 (95.6) | 338 (90.6) | 1438 (95.4) |
| Married | 8 (1.6) | 27 (4.4) | 35 (9.4) | 70 (4.6) |
| Teeth brushing | ||||
| No | 13 (2.6) | 8 (1.7) | 9 (2.4) | 30 (2.2) |
| Once a day | 258 (51.9) | 270 (57.7) | 207 (56.1) | 735 (55.1) |
| Twice a day | 185 (37.2) | 164 (35.0) | 134 (36.3) | 483 (36.2) |
| Three times a day | 41 (8.2) | 26 (5.6) | 19 (5.1) | 86 (6.5) |
| Drug use | ||||
| No | 511 (99.4) | 476 (99.4) | 66 (98.5) | 1053 (99.3) |
| Yes | 3 (0.6) | 3 (0.6) | 1 (1.5) | 7 (0.7) |
| Alcoholic drinks | ||||
| No | 495 (96.5) | 470 (97.9) | 41 (89.1) | 1006 (96.8) |
| Yes | 18 (3.5) | 10 (2.1) | 5 (10.9) | 33 (3.2) |
| Subjective sleep quality | ||||
| 0 | 14 (2.7) | 278 (44.9) | 111 (29.8) | 403 (26.7) |
| 1 | 67 (13.0) | 285 (46.0) | 219 (58.7) | 571 (37.9) |
| 2 | 303 (58.7) | 46 (7.4) | 34 (9.1) | 383 (25.4) |
| 3 | 132 (25.6) | 10 (1.6) | 9 (2.4) | 151 (10.0) |
| Sleep latency | ||||
| 0 | 119 (23.1) | 246 (39.7) | 81 (21.7) | 446 (29.6) |
| 1 | 242 (46.9) | 230 (37.2) | 175 (46.9) | 647 (42.9) |
| 2 | 119 (23.1) | 95 (15.3) | 88 (23.6) | 302 (20.0) |
| 3 | 36 (7.0) | 48 (7.8) | 29 (7.8) | 113 (7.5) |
| Sleep duration | ||||
| 0 | 137 (26.6) | 219 (35.4) | 76 (20.4) | 432 (28.7) |
| 1 | 189 (36.6) | 133 (21.5) | 120 (32.2) | 442 (29.3) |
| 2 | 132 (25.6) | 149 (24.1) | 116 (31.1) | 397 (26.3) |
| 3 | 58 (11.20) | 118 (19.1) | 61 (16.4) | 237 (15.7) |
| Habitation sleep efficiency | ||||
| 0 | 420 (81.4) | 507 (81.9) | 290 (77.7) | 1217 (80.7) |
| 1 | 69 (13.4) | 43 (6.9) | 51 (13.7) | 163 (10.8) |
| 2 | 12 (2.3) | 47 (7.6) | 20 (5.4) | 79 (5.2) |
| 3 | 15 (2.9) | 22 (3.6) | 12 (3.2) | 49 (3.3) |
| Sleep disturbances | ||||
| 0 | 110 (21.3) | 201 (32.5) | 70 (18.8) | 381 (25.3) |
| 1 | 386 (74.8) | 364 (58.8) | 262 (70.2) | 1012 (67.1) |
| 2 | 20 (3.9) | 30 (4.8) | 39 (10.5) | 89 (5.9) |
| 3 | - | 24 (3.9) | 2 (0.5) | 26 (1.7) |
| Use of sleeping medication | ||||
| 0 | 496 (96.1) | 563 (91.0) | 334 (89.5) | 1393 (92.4) |
| 1 | 10 (1.9) | 45 (7.3) | 22 (5.9) | 77 (5.1) |
| 2 | 8 (1.6) | 8 (1.3) | 9 (2.4) | 25 (1.6) |
| 3 | 2 (0.4) | 3 (0.5) | 8 (2.1) | 13 (0.9) |
| Daytime dysfunction | ||||
| 0 | 219 (42.4) | 390 (63.0) | 190 (50.9) | 799 (53.0) |
| 1 | 211 (40.9) | 174 (28.1) | 131 (35.1) | 516 (34.2) |
| 2 | 64 (12.4) | 48 (7.8) | 36 (9.7) | 148 (9.8) |
| 3 | 22 (4.3) | 7 (1.1) | 16 (4.3) | 45 (3.0) |
| Age | 19.22 ± 1.25 | 20.25 ± 1.28 | 21.30 ± 1.34 | 20.2 ± 1.5 |
| Anxiety | 7.53 ± 7.17 | 8.06 ± 9.55 | 8.37 ± 8.97 | 7.95 ± 8.6 |
| Exercise behavior | 9.73 ± 3.23 | 10.71 ± 3.39 | 9.93 ± 3.70 | 10.2 ± 3.4 |
| Regular behavior | 14.62 ± 3.32 | 14.45 ± 3.05 | 14.36 ± 3.31 | 14.5 ± 3.2 |
| Nutrition behavior | 13.98 ± 2.75 | 13.79 ± 2.73 | 13.99 ± 3.56 | 13.9 ± 3.0 |
| Health risk behavior | 16.68 ± 2.33 | 16.69 ± 2.13 | 16.50 ± 2.40 | 16.6 ± 2.3 |
| Health responsibility | 24.01 ± 3.35 | 23.38 ± 3.28 | 23.78 ± 3.80 | 23.7 ± 3.4 |
| Social support | 23.19 ± 3.31 | 21.98 ± 3.81 | 21.96 ± 4.05 | 22.3 ± 3.7 |
| Stress management | 17.75 ± 3.02 | 17.66 ± 2.78 | 17.75 ± 3.08 | 17.7 ± 2.9 |
| Life appreciation | 19.81 ± 3.04 | 19.09 ± 3.27 | 18.96 ± 4.10 | 19.3 ± 3.4 |
| HLSUS score | 139.78 ± 14.03 | 137.76 ± 14.37 | 137.24 ± 16.13 | 138.3 ± 14.7 |
4.2. Modelling the Students' Sleep Quality
AIC and BIC values were equal to 3790.68 and 3899.712 for panel linear regression model, and they were equal to 3793.043 and 3911.556 for the frontier model. Therefore, panel linear regression model was more powerful in modelling the students sleep quality.
Table 2 shows panel linear regression results in modelling the students sleep quality using sex, unit, residency, marital status, teeth brushing, drug use, alcoholic drinks, age, anxiety, and HLSUS score. The results indicated that residence, anxiety, and HLSUS score had a significant effect on sleep quality of medical students, such that the dormitory students had lower sleep quality than students who lived at home with their parents. Also, students' sleep quality decreased by increasing anxiety and decreasing HLSUS score.
| Variables | Coefficient | 95% CI | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | Ref. | - | - |
| Female | -0.27 | (-0.63, 0.10) | 0.149 |
| Unit | |||
| Faculty of health, nutrition and management | Ref. | - | - |
| Faculty of paramedical, nursing and midwifery | 0.08 | (-0.32, 0.49) | 0.690 |
| Faculty of medicine, medicine and dentistry | -0.13 | (-0.54, 0.27) | 0.526 |
| Residency | |||
| Dormitory | Ref. | - | - |
| At home with parents | -0.45 | (-0.79, -0.12) | 0.008 a |
| Personal single home | -0.34 | (-1.08, 0.39) | 0.363 |
| Marital status | |||
| Single | Ref. | ||
| Married | -0.76 | (-1.61, 0.08) | 0.077 |
| Teeth brushing | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Once a day | 0.20 | (-0.91, 1.31) | 0.726 |
| Twice a day | 0.30 | (-0.84, 1.43) | 0.608 |
| Three times a day | 0.01 | (-1.24, 1.25) | 0.988 |
| Drug use | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Yes | 1.74 | (0.02, 3.50) | 0.043 a |
| Alcoholic drinks | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Yes | -0.47 | (-1.41, 0.47) | 0.328 |
| Age | -0.08 | (-0.20, 0.03) | 0.163 |
| Anxiety | 0.08 | (0.07, 0.10) | < 0.001 a |
| HLSUS score | -0.02 | (-0.03, -0.01) | < 0.001 a |
a Values are statistically significant.
Since HLSUS has a significant effect on students sleep quality, the impact of HLSUS components was investigated. Table 3 shows panel linear regression results in modelling the students sleep quality using sex, unit, residency, marital status, teeth brushing, drug use, and HLSUS components including exercise behavior, regular behavior, nutrition behavior, health risk behavior, health responsibility, social support, stress management, and life appreciation. The results indicated that residency, drug use, anxiety, regular behavior, and health risk behavior affected the sleep quality of medical students significantly, so that the dormitory students and students using drugs had lower sleep quality than students who lived at home with their parents and did not use drugs, respectively. Furthermore, students' sleep quality decreased by increasing anxiety level and decreasing regular behavior and health risk behavior scores.
| Variables | Coefficient | 95% CI | P-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | Ref. | - | - |
| Female | -0.08 | (-0.46, 0.29) | 0.654 |
| Unit | |||
| Faculty of health, nutrition and management | Ref. | - | - |
| Faculty of paramedical, nursing and midwifery | 0.10 | (-0.29, 0.49) | 0.611 |
| Faculty of medicine, medicine and dentistry | -0.14 | (-0.54, 0.25) | 0.466 |
| Residency | |||
| Dormitory | Ref. | - | - |
| At home with parents | -0.41 | (-0.74, -0.07) | 0.018 a |
| Personal single home | -0.36 | (-1.07, 0.35) | 0.315 |
| Marital status | |||
| Single | Ref. | ||
| Married | -0.59 | (-1.42, 0.24) | 0.164 |
| Teeth brushing | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Once a day | 0.42 | (-0.68, 1.51) | 0.454 |
| Twice a day | 0.51 | (-0.62, 1.64) | 0.374 |
| Three times a day | 0.26 | (-0.98, 1.50) | 0.679 |
| Drug use | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Yes | 1.87 | (0.12, 3.62) | 0.036 a |
| Alcoholic drinks | |||
| No | Ref. | - | - |
| Yes | -0.80 | (-1.7, 0.15) | 0.097 |
| Age | -0.06 | (-0.17, 0.05) | 0.283 |
| Anxiety | 0.08 | (0.06, 0.10) | < 0.001 a |
| Exercise behavior | -0.03 | (-0.08, 0.02) | 0.252 |
| Regular behavior | -0.11 | (-0.17, 0.06) | < 0.001 a |
| Nutrition behavior | 0.05 | (-0.01, 0.12) | 0.127 |
| Health risk behavior | -0.09 | (-0.17, 0.02) | 0.009 a |
| Health responsibility | -0.04 | (-0.10, 0.01) | 0.126 |
| Social support | -0.01 | (-0.06, 0.04) | 0.789 |
| Stress management | -0.01 | (-0.07, 0.05) | 0.709 |
| Life appreciation | -0.01 | (-0.07, 0.05) | 0.694 |
a Values are statistically significant.
5. Discussion
This study was conducted to investigate the relationship between sleep quality and its potential predictors in university students. Consistent with the findings of previous studies, our study results showed that the mean PSQI score was 5.25 (SD = 2.00) (19), and nearly half of the students suffered from poor sleep quality (8, 20-23).
In the current study, type of residency was discovered to be a significant factor contributing to the sleep quality in university students, so that the dormitory students had lower sleep quality than the students who lived at home with their parents. Similarly, some previous studies indicated that sleep quality was lowest in dormitory students (8, 19); however, several other studies found no significant relationship between residency type and quality of sleep (10, 13, 22). The lower sleep quality in dormitory students may have been due to the stress caused by living away from family, the responsibility of living in a dormitory, and adaptation to different sleep patterns of their roommates.
Moreover, using drugs was another significant factor contributing to sleep quality in students, such that the students who used drugs had lower sleep quality than others. Previous studies generated similar results suggesting that drug users had lower sleep quality (11, 24). It was impossible to provide exact information due to the failure in identifying accurate substances. However, it was argued that using these unknown drugs may have been associated with poor sleep quality and had long-term, irreparable consequences.
In addition, the students' anxiety was inversely related to their sleep quality; that is, the students' sleep quality was improved with a decrease in their anxiety. This finding was consistent with that of previous studies (19, 25-28). Anxiety causes insomnia which in turns worsens the person's mood, leading to more disturbing thoughts. If this cycle continues, the sleep quality is then reduced due to the increased anxiety.
A close relationship was also detected between HLSUS score and the sleep quality in students. In other words, the students' sleep quality was improved with an increase in their HLSUS score. Further investigation revealed that the components of regular behavior and health risk behavior had a significant effect on students' sleep quality; however, the effects of other subscales were not significant. Wang et al. indicated that health responsibility and exercise behavior had no significant effect on sleep quality, but nutrition and stress management behaviors had significant effects on it (12). Moudi et al. found that nutrition, health responsibility, and stress management significantly affected the quality of sleep (29).
According to our study results which were inconsistent with the findings of previous studies, the sex, (7, 8, 13, 25, 27, 30) unit, (10, 25) marital status, (10, 13, 19, 27) teeth brushing, (31) alcoholic drinks (12, 32), and age (10, 11, 13, 22, 24, 25) were detected to have no significant effect on sleep quality in university students.
5.1. Strengths and Limitations
The present study faced some limitations. First, there was not information about the type of the drugs used by students; therefore, it was not possible to specify the mechanism of the effect of the drug on sleep quality. Second, some important information (e.g., depression level, smartphone dependence, and internet addiction) was not available to be included in the analysis and improve the fit of models. However, the present study successfully investigated the students from different faculties and disciplines of medical sciences and assessed their sleep quality and its predictors.
5.2. Conclusions
It was concluded that the sleep quality among university students was extremely poor. It was also found that sleep quality had a significant relationship with drug use, anxiety, and healthy lifestyle scale. Therefore, it was recommended that proper plans should be developed in order to improve students’ sleep quality by reducing their anxiety, increasing their awareness about drug use, and improving their lifestyle quality.