1. Context
Elder abuse, also called elder mistreatment or elder maltreatment, is “a single or repeated act or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any relationship where there is an expectation of trust that causes harm or distress to an older person” (1, 2). This type of violence includes: (i) Physical, sexual, psychological and emotional abuse; (ii) financial and material abuse; (iii) abandonment; (iv) neglect; and (v) serious loss of dignity and respect (3). The health consequences of elder abuse can be especially serious (4). It can destroy a victim’s quality of life by declining his functional abilities, increasing dependency, inducing dementia and enhancing the risk of malnutrition or over medication (5, 6). Elder abuse can even result in death.
Prospective studies have demonstrated that victims of elder abuse are at a higher risk for premature death than those not reporting abuse, especially in black populations (7, 8). Although elder mistreatment is not a new phenomenon, its formal recognition has only occurred over the last 20 to 30 years. A systematic literature review reported the prevalence of elder abuse in Asian countries ranged from 0.22 per 1000 to 62% (9). Yon et al. in a meta-analysis of various countries across the globe found a prevalence rate of 15.7% for elder abuse (10). Concern over the abuse of older adults has been heightened with the realization that the elderly population will increase dramatically in the coming decades (11). It is predicted that the proportion of the world’s population aged 60 years and older will nearly double from about 12% in 2015 to 22% in 2050 (12, 13). Iran is no exception in this regard.
In 2016, about 9.3% of Iran’s population was 60 years or over, and it is expected to rise to 30% by 2050 (14). In recent years, several studies have investigated elder abuse in different cities of Iran, but none has systematically summarized them. Hence, regarding the rapid growth of the aged people in this country and the importance of the elder abuse as a factor influencing older adults’ health and quality of life, this systematic review was conducted to assess the prevalence of elder abuse and its neglect in Iran. Understanding the magnitude of elder abuse is a crucial first step in the public health approach to prevent this type of violence (10). On the other hand, awareness about the frequency of elder abuse facilitates other related studies.
2. Objectives
The present systematic review and meta-analysis was performed to determine the prevalence of elder abuse and neglect in Iran.
3. Methods
3.1. Search Strategy
The following databases were searched between 10 March and 22 April 2018 to identify eligible articles: Magiran, Scientific Information Database (SID), Irandoc, Scopus, PubMed and Web of Science. Databases were searched with no time restriction. The following terms or a combination of them was used for searching in English electronic databases: “aged”, “elderly”, “older adults”, “senior aging”, “abuse”, “geriatric”, “elder abuse”, “elder neglect”, “elder misbehavior”, “elder mistreatment”, “violence”, “prevalence”, “cross-sectional”, “Iran” and “Iranian”. Boolean operators (AND, OR) were used wherever possible. Persian terms equivalent to the English terms mentioned above were used for searching in Persian electronic databases. Google Scholar was also searched to ensure that no article is missed. In a final search, the reference lists of all the included articles were also manually reviewed to identify any additional articles (snowball method). Unpublished studies were not searched in this review.
3.2. Study Selection Criteria
The selection process was conducted in three steps. First, the titles of all the collected articles were reviewed and duplicates were removed. Second, abstracts of all the articles that were somehow relevant to the study subject were collected. Finally, studies that investigated the prevalence of elder abuse and neglect in a sample of Iranian elderly population were included in this study. The following were excluded: (1) hospital-based studies, (2) studies with sample sizes less than 100, (3) studies that were not published as full reports like conference abstracts and (4) articles that were not available in their full text.
3.3. Data Extraction
The following information was extracted from studies that met the inclusion criteria: study characteristics (the first author, year of publication, year of study and location), study methodology (sampling method and the instrument used to measure elder abuse), characteristics of participants (age and gender), sample size, prevalence rates and other relevant information.
3.4. Quality Assessment
The quality of the included studies was assessed based on a modified version of the strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) checklist (15). This checklist consists of 22 items; scores on each item range from 0 to 2. A score of 2 is awarded if the “criterion was fully met”, 1 if the “criterion was partially met” and 0 if the “criterion was not met”. Scores of 0 - 22, 23 - 33 and 34 - 44 are defined as low, moderate and high quality, respectively.
3.5. Statistical Analysis
The standard errors were calculated by the following formula:
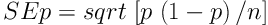
p is the proportion of successes in the sample and n is the number of observations in the sample. Data were analyzed using RevMan software, version 5.3 (16). Pooled estimates of the prevalence of elder abuse were calculated using the random-effects model.
4. Results
4.1. Literature Search
On the initial search, 1386 articles were retrieved. After excluding 374 duplicates and 992 irrelevant articles, 20 studies remained for full-text evaluation. Of these, seven studies were excluded because two of them did not contain prevalence information, two had a sample size of less than 100 subjects, one was an abstract from a conference, one was a hospital-based study and full text of the other articles was not available. Finally, 13 articles were considered for the systematic review (Figure 1).
4.2. Study Characteristics
The years the studies were performed and published ranged from 2007 to 2015 and from 2008 to 2017, respectively. The total number of participants was 4357, with a range of 180 to 500 per study. All the 13 included studies were cross-sectional and quantitative in nature. One study reported data only for females (17), while the remainder included male as well as female participants. Eight studies used the Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire (17-24), three (25-27) used a researcher-designed questionnaire and two studies (28, 29) used the elder assessment instrument. Nine studies (17-24, 27) provided past-year prevalence data for abuse and four (25, 26, 28, 29) provided prevalence data for any abuse that had occurred since the victims became older adults (i.e., aged 60 - 65 years and older; Table 1).
| First Author - Publication Year | Participants | Gender | Instruments to Assess Abuse | Prevalence Period | Method of Data Collection | Sampling Procedure | Prevalence Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Khalili - 2016 (22) | 500 people aged over 60 years, who had health care records in health centers in Kashan, Esfahan | 290 (58%) male, 210 (42%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 80% |
| Financial abuse = 45.6% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 45% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 41.2% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 37.8% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 35.6% | |||||||
| Emotional neglect = 29.8% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 22.2% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 16.6% | |||||||
| Morowatisharifabad - 2016 (23) | 250 people aged over 60 years in Yazd, Yazd | 126 (50.4%) male, 124 (49.6%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 79.6% |
| Emotional neglect = 66% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 52.4% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 44.8% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 42.8% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 16.4% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 15.6% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 8.4% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 4.4% | |||||||
| Mohebbi - 2016 (21) | 210 people aged over 60 years, who were referred to rural health centers in Dezful, Khuzestan | 116 (55.2%) male, 94 (44.8%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 60.5% |
| Emotional neglect = 38.6% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 22.8% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 15.3% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 14.3% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 14.3% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 12.4% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 12.9% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 7.3% | |||||||
| Keyghobadi - 2014 (17) | 180 people aged over 60 years, who were referred to mosques and clinics in Sabzevar, Khorasan Razavi | 180 (100%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 49.4% |
| Emotional neglect = 69% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 52% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 48.5% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 47.3% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 45.4% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 44.8% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 44.5% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 42.8 | |||||||
| Nori - 2014 (19) | 247 people aged over 60 years, who had health care records in urban or rural health centers in Kalaleh, Golestan | 137 (55.5%) male, 110 (44.5%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = - |
| Emotional neglect = 34.8% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 33.6% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 29.1% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 26.7% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 22.3% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 21.9% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 12.6% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 2.8% | |||||||
| Nassiri - 2016 (20) | 465 people aged over 60 years, who were referred to urban or rural health centers in Gorgan and Aq-Qala, Golestan | 253 (55.4%) female, 212 (44.6%) male | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 63.3% |
| Care neglect = 59.8% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 53.3% | |||||||
| Emotional neglect = 43% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 39.1% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 34% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 34% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 8.2% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 8% | |||||||
| Heravi Karimoei - 2012 (18) | 379 people aged over 65 years, who were members of the senior social clubs in Tehran, Tehran | 254 (67%) female, 125 (33%) male | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 25.9% |
| Emotional neglect = 17.4% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 17.2% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 14.8% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 10% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 9.8% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 7.9% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 4.7% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 3.7% | |||||||
| Kashfi - 2017 (24) | 226 people aged over 60 years, who were referred to urban healthcare and retirement centers in Shiraz, Shiraz | 61 (27.4%) male, 165 (72.6%) female | Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire | 1 year | Face-to-face interview + aelf-administered | Random sampling | Prevalence = - |
| Emotional neglect = 43.8% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 41.2% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 31.9% | |||||||
| Financial neglect = 28.8% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 23% | |||||||
| Authority deprivation = 20.8% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 7% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 4% | |||||||
| Manoochehri - 2009 (25) | 400 people aged over 60 years, who were referred to parks in Tehran, Tehran | 200 (50%) male, 200 (50%) female | Researcher-made questionnaire | Since aged 60 | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 87.8% |
| Psychological abuse = 84.8% | |||||||
| Neglect = 68.3% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 40.1% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 35.2% | |||||||
| Barzanjeh Atri - 2013 (26) | 415 elderly people aged over 60 years, who were referred to urban health centers in Tabriz, East Azerbaijan | 258 (62.2%) male, 157 (37.8%) female | Researcher-made questionnaire based on H-S/EAST and other related studies | Since aged 60 | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = - |
| Psychological abuse = 91% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 12.3% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 14.3% | |||||||
| Neglect = 29.9% | |||||||
| Alizadeh Khoei - 2014 (27) | 300 people aged over 60 years, who had health care records in urban health centers in Ahvaz, Khuzestan | 160 (53.3%) female, 140 (46.7%) male | Researcher- made questionnaire based on H-S/EAST | 1 year | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 14.7% |
| Physical abuse = 10.3% | |||||||
| Care neglect = 9% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse= 3% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 3% | |||||||
| Karimi - 2008 (28) | 385 people aged over 60 years, who were in urban public places in Ahvaz, Khuzestan | 205 (53.2%) female, 180 (46.8%) male | Elder assessment instrument | Since aged 60 | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 10.5% – 25% |
| Neglect = 31.7% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 25% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 16.9% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 12% | |||||||
| Physical abuse = 10.5% | |||||||
| Hosseini - 2016 (29) | 400 people aged over 60 years, who were in public places in Chaharmahal and Bakhtiari Province | 240 (60%) female, 60 (40%) male | Elder assessment instrument | Since aged 60 | Face-to-face interview | Random sampling | Prevalence = 17.1% |
| Physical abuse = 35.9% | |||||||
| Abandonment = 23.3% | |||||||
| Psychological abuse = 31.9% | |||||||
| Financial abuse = 14.3% | |||||||
| Neglect = 14.6% |
Abbreviation: H-S/EAST, Hwalek-Sengstock elder abuse screening test.
4.3. Estimated Prevalence of Elder Abuse
With regard to differences among instruments in assessing elder abuse, data originally used from 13 studies were on physical, psychological and financial abuse (17-29), 10 studies on abandonment (17-24, 28, 29), nine studies on care neglect (17-24, 27), eight studies on financial neglect, emotional neglect and authority deprivation (17-24), four studies on neglect (25, 26, 28, 29), and 10 studies on overall prevalence of elder abuse and neglect (17, 18, 20-23, 25, 27, 28). The overall rates across all forms of abuse ranged from 14.7% in a study from Ahvaz, Iran (27) to 87.8% in a study from Tehran, Iran (25). With regard to the different forms of abuse, a wide range of prevalence rates was again demonstrated. Rates of physical abuse ranged between 2.8 % (19) and 44.5% (17), psychological abuse ranged between 3% (27) and 91% (26), financial abuse ranged between 3% (16) and 48.5% (11), neglect ranged between 14.6% (29) and 68.3% (25), emotional neglect ranged between 17.4% (18) and 69% (17), care neglect ranged between 7.3% (21) and 59.8% (20), financial neglect ranged between 9.8% (18) and 44.8% (17), authority deprivation ranged between 10% (18) and 45.4% (17) and abandonment rates ranged between 3.7% (18) and 42.8% (17).
Eight studies were eligible to be included in the meta-analysis. The criteria for inclusion in the meta-analysis were: (1) Studies that used the same questionnaire and (2) studies that provided past-year prevalence data. Hence, only studies that used Iranian domestic elder abuse questionnaire were eligible for inclusion in the meta-analysis. For the prevalence estimates, we used data from eight studies on physical abuse, psychological abuse, financial abuse, emotional neglect, financial neglect, care neglect, authority deprivation and abandonment (10-24) and six studies on the overall prevalence of elder abuse and neglect (17, 18, 20-23).
The pooled prevalence rate for overall elder abuse was 60% (95% CI: 42% - 78%; Figure 2).
The pooled prevalence estimates in the domains of elder abuse were 13% (95% CI: 7% - 18%) for physical abuse, 36% (95% CI: 24% - 47%) for psychological abuse, 31% (95% CI: 18% - 43%) for financial abuse, 28% (95% CI: 19% - 37%) for financial neglect, 36% (95% CI: 22% - 50%) for care neglect, 43% (95% CI: 31% - 55%) for emotional neglect, 25% (95% CI: 16% - 35%) for authority deprivation and 13% (95% CI: 8% - 18%) for abandonment (Figure 3).
4.4. Quality of the Included Studies
The STROBE scores for the included studies ranged from 25 to 35 out of 44 points (moderate-to-high quality; Table 2).
| S. | Study Details | STROBE Items | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | Total Score | |
| 1 | Khalili, 2016 (22) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | □ | 34 |
| 2 | Morowatisharifabad, 2016 (23) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | Δ | Δ | Δ | □ | 33 |
| 3 | Mohebbi, 2016 (21) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | × | Δ | Δ | □ | 34 |
| 4 | Keyghobadi, 2014 (17) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | × | □ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | × | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | × | 28 |
| 5 | Nori, 2014 (19) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | × | □ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | Δ | × | Δ | Δ | × | 27 |
| 6 | Nassiri, 2016 (20) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | × | Δ | Δ | □ | 33 |
| 7 | Heravi Karimoei, 2012 (18) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | 35 |
| 8 | Manoochehri, 2009 (25) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | Δ | × | × | □ | × | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | × | □ | × | Δ | Δ | × | 25 |
| 9 | Barzanjeh Atri, 2013 (26) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | × | □ | × | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | × | Δ | Δ | × | 28 |
| 10 | Alizadeh Khoei, 2014 (27) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | Δ | × | Δ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | × | 30 |
| 11 | Karimi, 2008 (28) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | Δ | × | Δ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | × | □ | × | Δ | Δ | × | 27 |
| 12 | Hosseini, 2016 (29) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | □ | × | × | □ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | Δ | Δ | □ | Δ | Δ | × | 29 |
| 13 | Kashfi, 2017 (24) | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | × | Δ | × | □ | Δ | □ | □ | □ | □ | □ | Δ | □ | □ | Δ | Δ | □ | 35 |
a1, title and abstract; [Introduction] 2, background/rationale; 3, objectives; [Methods] 4, study design; 5, setting; 6, participants; 7, variables; 8, data sources/measurement; 9, bias; 10, study size; 11, quantitative variables; 12, statistical methods; [Results] 13, participants (groups); 14, descriptive data; 15, outcome data; 16, main results; 17, other analyses; [Discussion] 18, key results; 19, limitations; 20, interpretation; 21, generalizability; [Other Information] 22, funding.
b2 (□), good description; 1 (Δ), partial description; 0 (×), no description.
5. Discussion
This systematic review and meta-analysis study, based on a comprehensive search strategy, was conducted to better understand the prevalence of elder abuse and neglect in Iran. Thirteen studies were included in this review, of which eight studies were eligible to be included in the meta-analysis. Quality assessment showed that 4 (30.7%) studies had high quality and 9 (69.3%) studies had moderate quality. Of the articles reviewed, nine were published between 2014 and 2017. This growing rate shows that, in recent years, more attention has been paid to the study of elder abuse in Iran. The overall prevalence rates of abuse showed a high variability across studies, ranging from 14.7% to 87.8%. Although this systematic review identified 13 studies on prevalence, the meta-analysis only focused on studies that used the same questionnaire and reported estimates of past-year prevalence of elder abuse.
Findings from the meta-analysis revealed that the overall prevalence of elder abuse and neglect was 60%. Compared to the reported prevalence rates of elder abuse in other countries, this rate is close to those reported from some countries such as India (49%), Croatia (61.1%) and Peru (79.7%), but the rates reported from Ireland (2.2%), United Kingdom (2.6%), Canada (8.2%) and United States (10%) were considerably lower than the result of this review (30-36).
This review also found that prevalence estimates for abuse subtypes were highest for emotional neglect (43%), followed by psychological abuse (36%), care neglect (36%), financial abuse (31%), financial neglect (28%), authority deprivation (25%), abandonment (13%) and physical abuse (13%). A study in China showed that the prevalence rates of psychological abuse, caregiver neglect, physical abuse and financial abuse were 27.3%, 15.8%, 4.9% and 2.0%, respectively (37). In a national survey on elder abuse and neglect in Ireland, the prevalence rates of 1.3%, 1.2%, 0.5% and 0.3% were reported for financial abuse, psychological abuse, physical abuse and neglect, respectively (33). A study in Egypt reported that neglect was the most common type of abuse (42.4%), followed by physical abuse (5.7%), psychological abuse (5.1%) and financial abuse (3.8%) (38). The difference in the prevalence of elder abuse in various studies could be the result of different definitions of abuse, different sampling or recruiting methodologies, different instruments for assessing abuse, different levels of vulnerability of the surveyed older people and variability in communities’ characteristics and cultural contexts (39).
5.1. Limitations
This review has some limitations. Almost in all the included studies, elderly people were relatively healthy; thus, the results should be cautiously extrapolated to all country's older population. The difference in the questionnaires used in the studies was another limitation that prevented us from conducting a meta-analysis for all the available studies.
5.2. Conclusion
The present study revealed a high prevalence of elder abuse in Iran. The high prevalence of this problem shows that it is not enough to limit the support of the elderly to culture-building for families and religious teachings. Currently, there is less difference between the laws of ordinary people and the elderly in our country. Therefore, due to the rapid growth of the elderly population in the country, social protection and elderly-related legislation are two main issues for protecting the elderly as one of the most vulnerable strata. Also, due to the limited number of studies in this area in Iran, further research, especially in cities of provinces with large aging populations such as Guilan, is necessary. Studies aiming to assess the prevalence and influencing factors of abuse and negligence against elder people from the perspective of family members, home caregivers and professional nurses are recommended.


