1. Background
A generation ago, few thought that universities had much, if anything to do with entrepreneurship. The hard-earned freedom of the university won by the great German philosopher, scientist and scholar, von Humboldt, ensured that the university was not only liberated from the dictates of the church and state, but it guaranteed the value and primacy of “knowledge for its own sake”, rather than knowledge because it provides some value for society or the economy (1). Shane and Eckhardt (2010) assume that entrepreneurship is an orientation towards opportunity recognition (2) and that universities have a great role in doing so. University’s entrepreneurial role, taking advantage of opportunities that appear through its customary teaching and research missions as well as an emerging third mission to advance innovation, is fundamental rather than accidental (3). Etzkowitz focused on the entrepreneurial university concept at the beginning of 1983 in examining academic sciences of America and the use of studies in business environments (4). The entrepreneurial university is a university where the activities of all members, such as education, research, and so on are managed, administered and executed, so that the university is perceived as an institute or pseudo-economic firm i.e., the orientation of these activities for the profitability and gaining competitive economic advantages (5). A study by Stanford University in 2012 indicated that the companies founded by this university had an annual income of about $ 2.7 trillion, equal to the wealth of the tenth largest economy in the world (6). According to the existing developments and the emergence of learning society, presenting new models in higher education is an obvious fact. Development of entrepreneurship at the universities of medical sciences and health services is inevitable as they are the trustees and executors of a wide range of health care at prevention, treatment, rehabilitation and palliative levels and have the important mission of education and research at higher levels of medical sciences with many challenges in their approaches and management system (7).
Establishing an entrepreneurial university calls for a set of conditions: entrepreneurial strategic management of the organization, creating an environment where all students and employees tend to innovate and progress, universities understanding innovation and developing it as a more vital component of their strategy, the organizational structure of entrepreneurial university being formed of fewer layers, creation of a supportive system for transforming traditional culture into entrepreneurial culture, and payment tailored to performance. Moreover, it needs organizational culture, entrepreneurial cultures as important in empowering university staff enabling them to take advantage of their capabilities, senior management commitment, and management support. The different forms of support are supporting innovative ideas, providing the necessary resources or expertise, and institutionalizing entrepreneurial activities in systems and processes of the organization (8-14).
In explaining the causes of the emergence of entrepreneurial university, one can cite the response of universities to global changes and environmental pressures, the status of knowledge as a valuable source creating economic growth, and the move towards a knowledge-based economy as a new function of the university. Moreover, the causes are responding to new socioeconomic needs, new responsibility of the university towards society, social and economic development of the country and educational market (15-19).
Iranian universities were education-based up to the first decade after the Islamic Revolution (20). It seems that medical universities have a huge capacity to create and expand entrepreneurship in health care settings due to the diverse activities in health services. However, most of these universities do not have a specific organizational structure for designing and implementing educational, research and development programs to increase incentives and occasional entrepreneurial activities (21). The Ministry of Health and Medical Education emphasized the implementation of the project “Entrepreneurship Development Plan of Iranian Universities” at medical universities in March 2006. The board of ministers stressed establishing of the entrepreneurial offices in medical universities to implement the project. However, the implementation was not so successful because establishing an entrepreneurial university requires to initially identify conditions affecting entrepreneurship of universities (22).
Mahdavi Mazdeh et al. identified 10 conditions as the main indices of an entrepreneurial university: industry, business and management units, facilities and equipment, faculty members’ familiarity with entrepreneurship, training courses (entrepreneurship and related courses), curricula, teaching and presentation methods, entrepreneurship related journals, scientific and promotional conferences of entrepreneurship, learners’ activities, guild and extracurricular activities, and strategies of the university (23). In a paper about medical universities, Moghadasi et al. (22) identified nine conditions as effective in the entrepreneurship of universities: entrepreneurship, strategic priority of the university, entrepreneurship management at the university, briefing and entrepreneurship courses, promotion of entrepreneurial spirit and culture, funds, the activity of the society of students, equipment, the extracurricular activities, and academic curriculum programming. Faridi (24) found that for preparing Shahed University to become a third-generation university the status quo of the indices of goals and mission, management and leadership, entrepreneurship characteristics of teachers, and the entrepreneurial characteristics of employees and students is higher than the average, and more attention is needed to the indices of internal units and structures, relations with industries, financial institutions, commercialization and internationalization of education considering the actions taken.
According to a survey on five leading European universities, Clark (25) summarized the paths for organizational changes required for entrepreneurial universities: establishing a strong leadership nucleus, expanding structural boundaries, creating diversity in financial resources, establishing a strong academic base, and creating an integrated entrepreneurship culture throughout universities. In their study in America and Europe, Meyers and Pruthi (26) concluded that an entrepreneurial university consists of five key elements: leadership, a clear definition of entrepreneurial learning goals, directing curriculum, powerful internal and external networks, existence of innovation culture, experiential learning and knowledge transfer opportunities. Ketikidis et al. (27) conducted a study titled “An entrepreneurship model for higher education institutions: a study at the University of Sheffield International School.” The final model of the study consisted of four concepts of the effective structure of management and operations, the provision of distributed training, entrepreneurship and the spirit of innovation and internationalization as the strategic spirit and core. Furthermore, they understood that the organizational structure of the university and its entrepreneurial culture facilitated the strategic transformation of entrepreneurship in higher education. Garcia Aracil et al. (15) concluded that environmental indices, teaching, knowledge transfer, staff, financial resources, government, and management form an entrepreneurial university.
As stated, several studies have examined the subject of entrepreneurial university, but each examined one part of the subject. Most of them examined the components of an entrepreneurial university, some mentioned the creator of conditions, some others examined the strategies and operations of entrepreneurial university and others reviewed the achievements and outcomes of an entrepreneurial university.
The subject of entrepreneurship and entrepreneurial university at the present time is one of the important issues in the field of country management. In recent years, health sector has paid special attention to entrepreneurship, including 11 operational transformation and innovation packages in medical education as strategic policies of health education in the Islamic Republic of Iran. For this purpose, one of the topics that should be considered in the package on transformation and innovation in teaching of medical sciences is the focus on the transition package to the entrepreneurial university (28).
In this regard, universities of medical sciences have a mission to pursue four main goals based on entrepreneurial university model: to review and revise the mission, goals and functions of medical universities, to reform the structure of medical universities, to process engineering of medical universities and finally to develop infrastructures and resources of medical universities (29).
2. Objectives
We attempted to conduct a mixed method study using GT methodology for designing a model for entrepreneurial university to encompass the causal, context, and intervening conditions, core category, strategies and consequences validated and verified by experts.
3. Methods
Based on the analysis of the documents in the qualitative phase of this study that was 20 documents from the papers in the field of entrepreneurial university and interviews with the experts of entrepreneurial university, the main and subcategories related to entrepreneurial university and the final conceptual model were developed. In this stage, 12 people were selected as the sample using snowball sampling. Participants were from Razi University, Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University of Kermanshah, Kurdistan University of Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University of Sanandaj, Bu-Ali Sina University, Islamic Azad University of Hamedan and Islamic Azad University of Ilam. Data were collected through semi-structured face-to-face interviews. All participants had a Ph.D. degree. Each interview lasted 30 - 45 minutes. Interviews were conducted at the university or at participants’ workplaces. All the interviews were recorded, transcribed verbatim and analyzed according to conventional content analysis. The handwritten interviews were read several times to extract semantic units. The analysis units were reviewed several times and categorized on the basis of conceptual and semantic similarities by two coders. Main categories and subcategories were formed. The population in the qualitative section was faculty members with academic expertise or work experience in entrepreneurship, the members of the research club, the members of development centers of the universities, the members of the technology units, and the members of the communication offices with the industry based in the university. In the quantitative section with a population of 396, the sample size was determined as 195 according to Morgan’s table. Given the probability of dropouts and non-return of some questionnaires, the researcher distributed 20% more questionnaires, i.e. 235 questionnaires. Finally, 211 complete questionnaires were received and analyzed. The return rate for the questionnaires was approximately 90%. The sampling method in this phase was multi-stage clustering method. The data collection tool in the quantitative phase was a researcher-made questionnaire with the conditions of entrepreneurial university based on the results of the qualitative phase. The first part of the questionnaire was demographic characteristics of the subjects such as gender, education level, occupation history, and the province of service. The second part had 74 close-ended specialized questions prepared on a 5-option Likert scale. SPSS, LISREL and Partial Least Squares (PLS) software programs were used for quantitative analysis. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used to validate the questionnaire where the reliability of the whole questionnaire was 0.883. Content validity ratio (CVR) coefficient was used to evaluate content validity quantitatively. The opinions of 10 expert professors in the field of entrepreneurial university were used for calculating CVR. They were briefed on the objectives of the test and operational definitions related to the content of the questions, and were asked to answer each of the questions based on 3-option Likert scale: “the item is useful”, “the item is not useful” and “the item needs modification”. Then CVR was calculated as CVR = [nE-(N/2)]/(N/2); where, nE is the number of experts selecting “the item is useful”, and N is the total number of experts. The results showed that out of 87 items designed for entrepreneurial university variable, 74 items were identified as suitable and 13 items lacked adequate content validity and removed from the questionnaire. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was used to determine the construct validity and factor loadings for each of the main components of the entrepreneurial university questionnaire, used for the first time. The quantitative data collected through questionnaires were analyzed using descriptive and inferential statistics in two parts. First, general theories of statistics regarding demographic indices and variables were described using the frequency distribution table, the percentage of responses and graphs. Then, inferential statistics, CFA and path analysis were used to examine the construct validity.
According to structural equation model (SEM), CFA was used. Some of the model’s fitness indicators and their expected values are presented below:
Goodness of fit index (GFI) and adjusted goodness of fit index (AGFI): The GFI evaluates the relative value of variances and covariance by the model. GFI ranges between zero and one. GFI value must be equal to or greater than 0.90. AGFI is another fitness index for degree of freedom. This characteristic is equivalent to the application of the mean squares instead of the sum of squares in the form and denominator of the GFI. GFI and AGFI proposed by Jarzakag and Sorbum (1989) do not depend on the sample size.
Root mean square error of approximation (RMSEA): This indicator for good models is 0.05 or less, but in any case, it should be less than 0.1 and values that are more than 0.1 indicate poor fit.
NFI and CFI index: NFI index (also called the Benthaler Bounty index) is acceptable for values above 0.90 and is an indication of the fitness of the model. CFI greater than 0.90 is acceptable and is a sign of the fitness of the model.
The global quality standard introduced by Amato et al. in 2004 was used to examine the fitness of the model in PLS software. In this model, the value of GFI was 0.44, showing the fit for the SEM. Prior to the CFA, Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin measure of sampling adequacy (KMO) and Bartlett tests were used to ensure adequacy of sampling and data.
4. Results
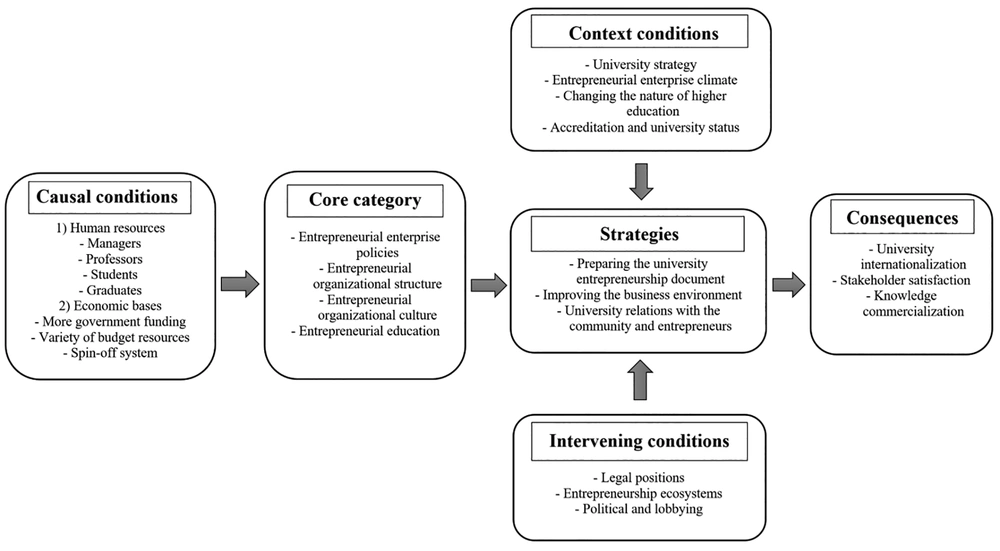
This model shows the relationships between causal conditions, core category, strategies, context conditions, intervening conditions and consequences (Figure 1). As seen in the model, causal conditions affect core category, context conditions, core category and intervening conditions affect the strategies, and the strategies affect consequences.
KMO value is 0.930, showing that the sample size is adequate for factor analysis (Table 1). In addition, the value of Bartlett test is significant at the level of 0.001, so the conditions for factor analysis are met.
| Sampling Adequacy Index | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KMO | Chi-Square | Degree of Freedom | P Value | |
| Bartlett test | 0.930 | 11776.877 | 2701 | < 0.001 |
The results of the first order CFA of entrepreneurial university construct separately for each of the components calculated (Table 2). All aspects of the structures of entrepreneurial university have a significant correlation with the components of this structure.
| Construct, Category, Items | Factor Loading | T Value | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causal conditions | |||
| Human resources | |||
| Being courageous and supporting the managers for university risk-taking | 0.69 | 10.34 | 0.01 |
| Economic foundations | |||
| Support for entrepreneurial university by getting funds from large corporations, independent institutions and foreign investors | 0.79 | 12.89 | 0.01 |
| Core category (entrepreneurial university) | |||
| Entrepreneurial enterprise policies | |||
| Referrals and references to upstream laws and documents to support entrepreneurial university | 0.69 | 10.69 | 0.01 |
| Overlap of entrepreneurship mission with university development plans | 0.69 | 10.64 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial organizational structure | |||
| Flexibility of the entrepreneurial university in responding to the changing demands and demands of the environment | 0.83 | 12.34 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial organizational culture | |||
| Efforts to coordinate and align entrepreneurship centers, accelerators and growth centers with one another | 0.79 | 11.66 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial Education | |||
| The idea-oriented research of entrepreneurial university and their commercialization | 0.66 | 9.29 | 0.01 |
| Compiling contents and syllabus of entrepreneurship-based courses based on community needs | 0.71 | 9.97 | 0.01 |
| Context conditions | |||
| University strategy | |||
| Establishment and expansion of industrial, service and production institutions by universities | 0.56 | 8.49 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial university student graduation condition based on their entrepreneurship | 0.73 | 11.87 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial Enterprise Climate | |||
| Learner-teaching nature of entrepreneurial university | 0.51 | 7.49 | 0.01 |
| Formation of entrepreneurship councils at the university with the participation of entrepreneurs | 0.79 | 11.68 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial attitude | |||
| Creating a positive attitude towards politicians and planners on the employment capacity of entrepreneurial university | 0.61 | 9.22 | 0.01 |
| Risk-taking | |||
| Creating a risk-taking environment for professors and students to encourage and endure failures and mistakes | 0.65 | 10.12 | 0.01 |
| Changing the nature of higher education | |||
| The evolving nature of changing the system of higher education to meet the society needs | 0.61 | 9.26 | 0.01 |
| Creation of jobs and wealth by the university | 0.68 | 10.64 | 0.01 |
| Accreditation and university status | |||
| Maintaining the competitive advantage of the university and preventing the collapse of the entrepreneurial university | 0.67 | 9.83 | 0.01 |
| Increase in demand for entry into the university and as a result of its credit enhancement | 69 | 10.07 | 0.01 |
| Strategies | |||
| Preparing the university entrepreneurship document | |||
| Developing strategies and implementation plans based on the university's entrepreneurship document and vision | 0.77 | 12.30 | 0.01 |
| Improving the business environment | |||
| Creating an economic boom and vitality in society by entrepreneurial university | 0.73 | 11.64 | 0.01 |
| Turning university entrepreneurship products into wealth | 0.72 | 11.22 | 0.01 |
| University relations with the community and entrepreneurs | |||
| Modeling a leading and top university in the field of entrepreneurship | 0.80 | 12.85 | 0.01 |
| Intervening conditions | |||
| Legal positions | |||
| University's authority in decision making (program design and how units function) | 0.80 | 13.07 | 0.01 |
| Legal form of the university in terms of being governmental or private | 0.86 | 14.46 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurship ecosystems | |||
| The role and effect of government and governmental organizations and politicians in creating an entrepreneurial university | 0.62 | 9.27 | 0.01 |
| The role and effect of investors in creating an entrepreneurial university | 0.69 | 10.65 | 0.01 |
| Political and lobbying | |||
| The role of political behaviors and lobbying policy makers (government officials and legislators), industry owners and academics on entrepreneurial university | 0.79 | 12.33 | 0.01 |
| Consequences | |||
| University internationalization | |||
| Encouraging and supporting successful entrepreneurs and promoting and disseminating local and international entrepreneurship | 0.75 | 11.94 | 0.01 |
| Stakeholder satisfaction | |||
| The effective role of graduates of entrepreneurial university in creating employment and elimination of unemployment in society | 0.77 | 12.41 | 0.01 |
| Knowledge commercialization | |||
| The tendency of faculty members to create productive businesses | 0.64 | 9.71 | 0.01 |
The values of all fitness indices are significant (Table 3). In this part, factor analysis of the entrepreneurial university questionnaire is dealt with in general. The questionnaire had six main structures (causal conditions, core category, context conditions, intervening conditions, strategies and consequences), each of which had some components examined below.
| Fitness Indices, Construct | χ2/df | GFI | AGFI | NFI | CFI | RFI | RMR | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptable fitness | < 3 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | < 0.05 | < 0.08 |
| Calculated fitness | ||||||||
| Causal conditions | 2.137 | 0.96 | 0.92 | 0.97 | 0.99 | 0.96 | 023 | 0.074 |
| Core category | 2.304 | 0.92 | 0.90 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.032 | 0.079 |
| Context conditions | 2.052 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.96 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.032 | 0.071 |
| Strategies | 2.122 | 0.94 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.026 | 0.073 |
| Intervening conditions | 2.020 | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.95 | 0.029 | 0.070 |
| Consequences | 1.936 | 0.95 | 0.90 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.96 | 0.021 | 0.067 |
Abbreviations: RFI, relative fit index; RMR, root mean square residual.
All variables of “entrepreneurial university” have a significant correlation with their related aspects (Table 4). In other words, SEM shows that all components have significant factor loadings with its dimensions. Thus, one can judge that all the references used to measure the structure of the university have acceptable fitness.
| Construct, Items | Factor Loading | T Value | P Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Causal conditions | |||
| Human resources | 0.84 | 14.58 | 0.01 |
| Economic foundations | 0.88 | 15.60 | 0.01 |
| Core category | |||
| Entrepreneurial enterprise policies | 0.88 | 16.04 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial organizational structure | 0.79 | 13.36 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial organizational culture | 0.81 | 13.95 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial education | 0.71 | 11.59 | 0.01 |
| Context conditions | |||
| University strategy | 0.85 | 15.07 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial enterprise climate | 0.80 | 13.70 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurial attitude | 0.86 | 15.62 | 0.01 |
| Risk-taking | 0.77 | 12.98 | 0.01 |
| Changing the nature of higher education | 0.83 | 14.62 | 0.01 |
| Accreditation and university status | 0.74 | 12.27 | 0.01 |
| Intervening conditions | |||
| Preparing the university entrepreneurship document | 0.79 | 13.38 | 0.01 |
| Improving the business environment | 0.81 | 14.02 | 0.01 |
| University relations with the community and entrepreneurs | 0.83 | 14.50 | 0.01 |
| Strategies | |||
| Legal positions | 0.76 | 12.48 | 0.01 |
| Entrepreneurship ecosystems | 0.81 | 13.69 | 0.01 |
| Political and lobbying | 0.72 | 11.66 | 0.01 |
| Consequences | |||
| University internationalization | 0.84 | 14.49 | 0.01 |
| Stakeholder satisfaction | 0.78 | 12.82 | 0.01 |
| Knowledge commercialization | 0.77 | 12.66 | 0.01 |
The CFA model that indicates the second-order model has a good fit (Table 5).
| Fitness Index | χ2/df | GFI | AGFI | NFI | CFI | RFI | RMR | RMSEA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acceptable fitness | < 3 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | > 0.90 | < 0.05 | < 0.08 |
| Calculated fitness | 2.114 | 0.91 | 0.89 | 0.97 | 0.98 | 0.97 | 0.015 | 0.073 |
Abbreviations: AGFI, adjusted goodness of fit index; GFI, goodness of fit index; RFI, relative fit index; RMR, root mean square residual; RMSEA, root mean square error of approximation.
5. Discussion
The purpose of the study was to validate the entrepreneurial university model. Qualitative data analysis was conducted through GT approach based on standard strategy through three encoding stages: open, axial, and selective. The results indicated that 21 components were placed in six main aspects of GT. The first aspect, core category, has four subcomponents of organizational policies, entrepreneurial organizational structure, entrepreneurial organizational culture, and entrepreneurial education and research. Entrepreneurship development, open policies of the university, creating business clusters, creating safe working environment, strategic planning, application of the system approach, reforming upstream policies, and the set of organizational policies of entrepreneurial university were in line with enhancing entrepreneurship. This component was similar to the studies by Yadollahi Farsi et al. (19) and Graham (30). Organic structure, university flexibility, transparent and bilateral communication, reduction in formalism, school autonomy, science and technology parks, and industry relations office were among the interviewees’ suggestions about the characteristics of the structure of entrepreneurial university. The common values of professors and students, the accreditation of entrepreneurship, the balance of professional activities with the value of the university, and the coordination of the three institutes involved in entrepreneurship at the university (entrepreneurship centers, accelerators and growth centers) were among the points the experts emphasized. This finding is in line with the studies by Salamzadeh et al. (31), Kordnaiej et al. (32), Yadollahi Farsi et al. (33) and Sporn (34). Demand-oriented nature of academic studies, designing project-oriented contents, merit-oriented evaluation, changing course syllabuses and updating curriculum and teaching methods, commercializing dissertation, formulating behavioral goals based on merit, networking and customer-oriented projects were among the conditions of entrepreneurship education, which were in line with the studies by Behzadi et al. (35) and Yadollahi Farsi et al. (33).
The second aspect, the causal conditions, includes two components: human resources and economic foundations. They mentioned four categories of managers, professors, students and graduates in the human resources department, each of which must have some characteristics and features. Entrepreneurial university managers should have an entrepreneurial approach and have a high commitment to supporting and implementing entrepreneurial university policies. Professors should have positive and consistent attitudes towards entrepreneurship and recruiting and admitting academic boards based on entrepreneurship. In addition, the student’s graduation condition should be conducting projects and creating employment. This is in line with the studies by Clark (25), Sporn (34), and Kordnaiej et al. (32). The interviewees stated the following conditions on the economic foundations such as diversity of university budget sources, attracting domestic and foreign capital, attracting more funds from the government, attracting funds from independent financial institutions and large companies, identifying entrepreneurship supporters and increasing the number of supporters of entrepreneurship, giving loans to graduates, spin off system, helping create graduate employment, incubators, and earning money through creation of affiliated businesses, services, and manufacturing. Salamzadeh et al. (31), Behzadi et al. (35) and Clark (25) have also mentioned these points in their studies.
The third aspect, context conditions, was university strategy, entrepreneurial organizational climate, entrepreneurship, and entrepreneurial attitude, risk-taking, changing the nature of higher education, and the credibility and status of the university. Cases such as project-orientation, group-orientation instead of self-orientation, and encouraging graduates for industrial research with society are parts of entrepreneurial university strategy, which was in line with the results of Zhou and Lu (36). Learning university, entrepreneurial university environment, creating accelerators and startups, and conducting sessions for presenting ideas were among the cases that covered the organizational climate aspect. The attitude and belief of the policymakers, students and graduates about the importance and necessity of creating an entrepreneurial university, and the belief that the university could help the industry sector covered the entrepreneurial attitude, in line with the studies by Guerrero and Urbano (37). Creating an environment that encourages risk-taking profile of university students and bears their failures and the mistakes, the existence of risk-taking managers and encouraging risk-taking faculty and students were among the concepts that were confirmed by the experts. The nature of the university has changed and the people believe so much in the university that they expect success in every project or topic where the university is involved.
The fourth aspect, intervening conditions, encompassed the sub-components of legal positions, entrepreneurial ecosystems, and politics and lobbying. The legal form of the university regarding being public or non-public, the legal frameworks and public policies of the government were among the issues that participants considered among the sub-components of legal positions. This was in line with the results of Yadollahi Farsi et al. (19). Experts divided entrepreneurship ecosystems into two ecosystems: controlled and uncontrolled ecosystems, of which propagators, accelerators, growth centers, startups, media, investors and policy makers can be cited. The political behavior and lobbying of academics, policymakers and industries, university decision-making power, informal communication and external organizational coalitions were among the concepts that show the importance of this component in the process of converting universities to entrepreneurial universities according to research experts, which was in line with the studies by Yadollahi Farsi et al. (19).
The strategies were the components of document preparation and the prospect of entrepreneurial university, in line with the studies by Salamzadeh et al. (31), Kordnaiej et al. (32), and Sporn (34), and improving the business environment and connection of the university with the community and entrepreneurs were in line with the studies by Yadollahi Farsi et al. (19). The outcomes were the internationalization of the university and the stakeholders’ satisfaction, consistent with the studies by Salamzadeh et al. (31) and the commercialization of knowledge as a paradigmatic model.
The model was tested in two steps. First-order factor analysis results showed a strong and good relationship between latent variables and the questionnaire. To study the second reliability criterion of the items, the significance of factor loadings was obtained according to t-statistic, where the values more than 1.96 at significance levels of 0.05 and more were significant. According to the results, all of the questionnaire items were effective in the variables.
Second-order factor analysis was assigning latent variables (21 items) to larger composites: causal conditions, core category, intervening conditions, context conditions, strategies and consequences. The results showed that all the items used for measuring these structures were significant at 99% confidence level. Accordingly, the second-order measuring model had a satisfactory fitness.
Finally, GFI quality criterion was used to examine the model fit in PLS. The values of GFI was 0.44, showing that the overall fitness of the SEM above the average and that the model is well explained by PLS.
5.1. Conclusions
According to the results of theoretical and research studies examined here, the results of this study are supported by previous ones. This model is applicable to all universities of Iran, including medical universities and other universities. Undoubtedly, using this model can facilitate the transfer of universities from the second generation to the third generation.